Electric bikes are motorized bicycles equipped with electric motors that assist riders in pedalling. They use rechargeable batteries to provide additional power, making cycling easier and more efficient.
Unleashing a new era of eco-friendly commuting, electric bikes have become the buzz of the town. But are they considered motor vehicles? Buckle up as we explore the intriguing intersection of pedal power and electric propulsion. Whether you’re a cycling enthusiast or just curious, let’s navigate the blurred lines where innovation meets the open road.
Electric bikes, also known as e-bikes, are not classified as motor vehicles in most jurisdictions. Generally, they are considered bicycles because they rely on a combination of human pedalling and electric assistance, with maximum speed limits typically ranging from 20 to 28 miles per hour. Regulations may vary, so it’s essential to check local laws to ensure compliance.
Different Types Of Electric Bikes
Electric bikes, also known as e-bikes, come in various types to suit different preferences and needs. Two common categories are pedal-assist and throttle-controlled electric bikes.
1. Pedal-Assist Electric Bikes:
How they work: These bikes are equipped with a pedal-assist system, also known as Pedelec (Pedal Electric Cycle). When you pedal, the electric motor provides additional power to make cycling easier.
Modes: Pedal-assist bikes often come with multiple assistance levels that riders can choose based on their desired level of support.
Benefits: Riders can enjoy the benefits of exercise while getting a boost from the motor, making it easier to tackle hills or cover longer distances with less effort.
2. Throttle-Controlled Electric Bikes:
How they work: Throttle-controlled e-bikes operate similarly to traditional scooters or motorcycles. A handlebar-mounted throttle allows the rider to control the electric motor’s power output without pedalling.
Modes: Some models may have variable speed settings or modes to control the level of electric assistance provided by the motor.
Benefits: Throttle-controlled e-bikes are user-friendly, especially for those who want a more relaxed riding experience without the need for constant pedalling. They are suitable for various riding scenarios, such as commuting or leisurely rides.
Electric Bike Laws By State
Research Your State Laws:
- Start by looking up your state’s specific laws regarding electric bikes. These regulations can vary, so understanding the rules applicable to your area is crucial.
Classify Your E-Bike:
- Identify the classification of your electric bike, as regulations often depend on factors like maximum speed and motor power. E-bikes are generally categorized into classes (Class 1, 2, or 3), influencing where they are allowed and any age restrictions.
Understand Helmet Requirements:
- Many states have helmet laws for electric bike riders, and the specifics may differ. Find out whether helmets are mandatory and if there are age-related requirements for riders.
Check Riding Locations:
- Determine where you can ride your electric bike. Some states allow e-bikes on bike paths and trails, while others restrict them to roads. Understanding these limitations ensures you ride safely and legally.
Stay Informed and Updated:
- Keep yourself informed about any changes to electric bike laws in your state. Regulations can evolve, so staying up-to-date ensures you remain compliant with the latest rules.
Class 1 Electric Bike Laws
- Age Requirement: To ride a Class 1 electric bike legally, riders typically need to be a certain age, often 16 or older, depending on local regulations.
- Motor Assistance Limit: Class 1 e-bikes are equipped with a motor that provides assistance only when the rider is pedalling and ceases to assist when the bike reaches a speed of around 20 mph (32 km/h).
- Helmet Usage: In many jurisdictions, wearing a helmet is mandatory for riders of Class 1 electric bikes, ensuring safety while enjoying the benefits of electric assistance.
Class 2 Electric Bike Laws
- Check Local Regulations: Before riding a Class 2 electric bike, familiarize yourself with local laws regarding its usage, as regulations may vary by region.
- Limit Speed to 20 mph: Class 2 electric bikes are typically capped at 20 mph in electric-only mode. Ensure you adhere to this speed limit to comply with Class 2 regulations.
- Use Electric Assistance: Class 2 e-bikes come with pedal-assist and/or throttle features. To comply with the law, operate the bike with electric assistance, either through pedalling or using the throttle, without exceeding the specified speed limit.
Class 3 Electric Bike Laws
- Always wear a helmet: Class 3 electric bikes are required to be equipped with a helmet, and riders must wear it at all times while operating the bike.
- Follow speed limits: Class 3 electric bikes are permitted to reach speeds up to 28 miles per hour, but riders must adhere to local speed limits to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
- Respect bike paths: When using Class 3 electric bikes, be aware of designated bike paths and follow traffic rules to ensure a smooth and safe experience for both riders and pedestrians.
Can A 13-Year-Old Ride An Electric Bike
Yes, a 13-year-old can ride an electric bike, but it’s essential to consider safety guidelines and local regulations. Electric bikes, often known as e-bikes, come in various models and power levels. Some may have age and speed restrictions, so it’s crucial to check the specific requirements for the particular e-bike in question. Understanding how electric bikes charge is important for both the rider and the responsible adults involved in their use.
Wearing a helmet is always a must for riders of any age to ensure safety. Parents or guardians should supervise and guide to ensure that the young rider follows traffic rules and practices responsible biking. Before letting a 13-year-old ride an electric bike, it’s advisable to consult local laws and the bike’s manual for any age-specific restrictions or recommendations.
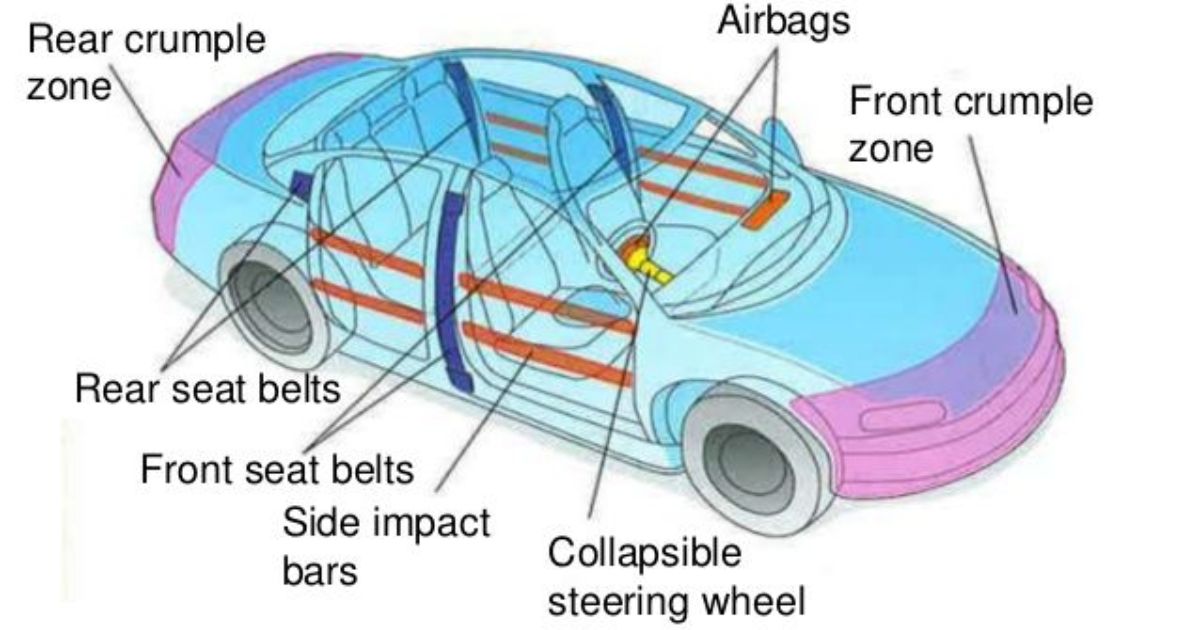
Comparison Of Safety Features With Traditional Motor Vehicles
| Safety Feature | Electric Scooters | Traditional Motor Vehicles |
| Seatbelts | Not applicable | Present in most vehicles |
| Airbags | Not common | Standard in many vehicles |
| Crumple Zones | Absent | Designed for collision safety |
| ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) | Not always present | Common in modern vehicles |
| Vehicle Size | Compact and smaller | More substantial |
| Speed | Generally lower | Varied, includes high speeds |
| License Requirements | May not require a license | Typically requires a license |
| Emissions | Environmentally friendly | Emit pollutants |
An Electric Scooter Considered A Motorized Vehicle
An electric scooter is classified as a motorized vehicle because it is powered by an electric motor. Unlike traditional scooters that run on gasoline, electric scooters use rechargeable batteries to generate power. These compact and eco-friendly vehicles have gained popularity for their ease of use and low environmental impact.
With a simple design and electric propulsion, they provide a convenient mode of transportation for short distances. Although they may not have the same power as larger motorized vehicles, electric scooters are subject to similar traffic rules and regulations to ensure safety on the roads. Riding an electric scooter responsibly involves obeying traffic signals, wearing appropriate safety gear, and being mindful of pedestrians and other vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I ride an electric bike on bike paths?
In most cases, yes. Electric bikes are typically allowed on bike paths, but it’s important to be aware of local regulations, as rules may vary.
Do electric bikes have a maximum speed limit?
Yes, electric bikes are usually designed with a maximum speed limit, often around 20-28 miles per hour (32-45 kilometres per hour). This helps maintain safety and compliance with regulations.
Are there age restrictions for riding electric bikes?
Age restrictions vary by location. In many places, there are no specific age requirements, but it’s essential to check local regulations, especially for more powerful electric bikes that might have age restrictions.
Conclusion
Electric bikes are generally not classified as motor vehicles. Instead, they are often categorized as electric bicycles or e-bikes. The distinction lies in factors such as their limited speed capabilities, pedal-assist nature, and compliance with specific regulations that define them as bicycles rather than traditional motor vehicles.
E-bikes offer a sustainable and convenient mode of transportation, blending the benefits of cycling with electric assistance, making them a popular choice for eco-conscious commuters and recreational riders alike. It’s essential to be aware of local laws and regulations regarding electric bikes, as these may vary in different regions.

I’m passionate electric scooter enthusiast and the voice behind this blog. I’m here to share my expertise and insights with you. From in-depth reviews to problem-solving guides, my goal is to help you make the most of your electric scooter experience.











![Gomyfinance.com Invest: I Made $5,000 in My First Month [Real Results 2025]](https://electopolo.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Gomyfinance.com-Invest-I-Made-5000-in-My-First-Month-Real-Results-2025-150x150.jpg)


